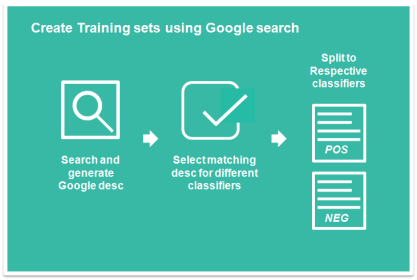
Morningstar.com provides useful information of stocks particularly financial ratio such as EPS, P/E etc breakdown to span of several years. It also provides an option for user to export all the data to a .csv file. This can be achieved by pressing the “export” button on the particular stock page. However, if there is a need to retrieve a series of stock data, users will have to visit the corresponding stock page and download the data one by one.
Below post is one way to retrieve the historical financial data of all target stocks. The first step will be to obtain the request url to activate the download without physically pressing the “export” button. To obtain the url, you can use the developer tools under Chrome web browser, press the network tab and monitor the ALL tab. Once the export button is pressed, the ALL tab will display the url corresponding to the request send. Example fo the url use for the request is as followed:
http://financials.morningstar.com/ajax/exportKR2CSV.html?&callback=?&t=XSES:N4E®ion=sgp&culture=en-US&cur=&order=asc
The blue section is the stock symbol. By changing the stock symbol, we can use the same url to retrieve all the financial data for different stocks. The url formation will be similar to what is mentioned in previous posts and the downloading can be achieved using python pattern module. After downloading the .csv file, the data can be post processed using python pandas.
Normally, the data will be easier to process if the data can be made into a Pandas Dataframe object which will then be used for joining and transforming purpose. However, the raw data downloaded (one csv for each stock) has all the headers in the first column instead of along the rows so we would need to transpose the data set. However, once transpose, the pandas will not be able to take care of columns that are non-unique. It can handle duplicate columns easily the moment it read from a csv file so the easy way is to re-write the transpose data back to the same file and read back the data again. Once read back using the Pandas.read_csv function, the result will be a dataframe object with the duplicate columns being taken care of. The columns can be rename after that for more desired column names. Below shows the section of code that does this.
def process_dataset(self):
""" Processed the data set by converting the csv to dataframe and attached the information for various stocks.
"""
## Rows with additional headers are skipped
try:
self.target_stock_data_df = pandas.read_csv(self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv, header =2, index_col = 0, skiprows = [19,20,31,41,42,43,48,58,53,64,65,72,73,95,101,102])
except:
print 'problem downloading files. '
self.target_stock_data_df = self.target_stock_data_df.transpose().reset_index()
self.target_stock_data_df["SYMBOL"] = self.com_data_stock_portion_url
#after transpose save back to same file and call again for column duplication problem
self.target_stock_data_df.to_csv(self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv_transpose, index =False)
self.target_stock_data_df = pandas.read_csv(self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv_transpose)
#rename columns
self.target_stock_data_df.rename(columns={'Year over Year':'Revenue yoy','3-Year Average':'Revenue 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average':'Revenue 5yr avg','10-Year Average':'Revenue 10yr avg',
'Year over Year.1':'Operating income yoy','3-Year Average.1':'Operating income 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average.1':'Operating income 5yr avg','10-Year Average.1':'Operating income 10yr avg',
'Year over Year.2':'Net income yoy','3-Year Average.2':'Net income 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average.2':'Net income 5yr avg','10-Year Average.2':'Net income 10yr avg',
'Year over Year.3':'EPS yoy','3-Year Average.3':'EPS 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average.3':'EPS 5yr avg','10-Year Average.3':'EPS 10yr avg',},
inplace =True)
if len(self.com_data_allstock_df) == 0:
self.com_data_allstock_df = self.target_stock_data_df
else:
self.com_data_allstock_df = pandas.concat([self.com_data_allstock_df,self.target_stock_data_df],ignore_index =True)
Once the data frame is formed, it can be used to perform various analysis such as checking if the stock have positive EPS growth over the years or the trend of P/E over the years. Below code include the get_trend function that will look at the historic EPS over time and whether it improves over time for a particular company.
import re, os, sys, math, time, datetime, shutil
import pandas
from pattern.web import URL, DOM, plaintext, extension, Element, find_urls
class MS_StatsExtract(object):
"""
Using morning star ajax call.
Can only get one stock at a time.
"""
def __init__(self):
""" List of url parameters -- for url formation """
self.com_data_start_url = 'http://financials.morningstar.com/ajax/exportKR2CSV.html?&callback=?&t=XSES:'
self.com_data_stock_portion_url = ''
self.com_data_stock_portion_additional_url = ''# for adding additonal str to the stock url.
self.com_data_end_url = '®ion=sgp&culture=en-US&cur=&order=asc'
self.com_data_full_url = ''
self.stock_list = ''#list of stock to parse.
## printing options
self.__print_url = 0
## temp csv storage path
self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv = r'c:\data\temp\ms_stats.csv'
self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv_transpose = r'c:\data\temp\ms_stats_t.csv'
## Temp Results storage
self.target_stock_data_df = object()
## full result storage
self.com_data_allstock_df = pandas.DataFrame()
self.hist_company_data_trends_df = pandas.DataFrame()
def set_stock_sym_append_str(self, append_str):
""" Set additional append str to stock symbol when forming stock url.
Set to sel.cur_quotes_stock_portion_additional_url.
Mainly to set the '.SI' for singapore stocks.
Args:
append_str (str): additional str to append to stock symbol.
"""
self.com_data_stock_portion_additional_url = append_str
def set_target_stock_url(self, stock_sym):
""" Set the target stock. Single stock again.
Set to self.com_data_stock_portion_url
Args:
stock_sym (str): Stock symbol.
"""
self.com_data_stock_portion_url = stock_sym
def set_stocklist(self, stocklist):
""" Set list of stocks to be retrieved.
Args:
stocklist (list): list of stocks to be retrieved.
"""
self.stock_list = stocklist
def form_url_str(self):
""" Form the url str necessary to get the .csv file
May need to segregate into the various types.
Args:
type (str): Retrieval type.
"""
self.com_data_full_url = self.com_data_start_url + self.com_data_stock_portion_url +\
self.com_data_end_url
def get_com_data(self):
""" Combine the cur quotes function.
Formed the url, download the csv, put in the header. Have a dataframe object.
Each one is one stock.
"""
self.form_url_str()
if self.__print_url: print self.com_data_full_url
## here will process the data set
self.downloading_csv()
def downloading_csv(self):
""" Download the csv information for particular stock.
"""
self.download_fault = 0
url = URL(self.com_data_full_url)
f = open(self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv, 'wb') # save as test.gif
try:
f.write(url.download())#if have problem skip
except:
if self.__print_download_fault: print 'Problem with processing this data: ', self.com_data_full_url
self.download_fault =1
f.close()
def process_dataset(self):
""" Processed the data set by converting the csv to dataframe and attached the information for various stocks.
"""
## Rows with additional headers are skipped
try:
self.target_stock_data_df = pandas.read_csv(self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv, header =2, index_col = 0, skiprows = [19,20,31,41,42,43,48,58,53,64,65,72,73,95,101,102])
except:
print 'problem downloading files. '
self.target_stock_data_df = self.target_stock_data_df.transpose().reset_index()
self.target_stock_data_df["SYMBOL"] = self.com_data_stock_portion_url
#after transpose save back to same file and call again for column duplication problem
self.target_stock_data_df.to_csv(self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv_transpose, index =False)
self.target_stock_data_df = pandas.read_csv(self.ms_stats_extract_temp_csv_transpose)
#rename columns
self.target_stock_data_df.rename(columns={'Year over Year':'Revenue yoy','3-Year Average':'Revenue 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average':'Revenue 5yr avg','10-Year Average':'Revenue 10yr avg',
'Year over Year.1':'Operating income yoy','3-Year Average.1':'Operating income 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average.1':'Operating income 5yr avg','10-Year Average.1':'Operating income 10yr avg',
'Year over Year.2':'Net income yoy','3-Year Average.2':'Net income 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average.2':'Net income 5yr avg','10-Year Average.2':'Net income 10yr avg',
'Year over Year.3':'EPS yoy','3-Year Average.3':'EPS 3yr avg',
'5-Year Average.3':'EPS 5yr avg','10-Year Average.3':'EPS 10yr avg',},
inplace =True)
if len(self.com_data_allstock_df) == 0:
self.com_data_allstock_df = self.target_stock_data_df
else:
self.com_data_allstock_df = pandas.concat([self.com_data_allstock_df,self.target_stock_data_df],ignore_index =True)
def get_com_data_fr_all_stocks(self):
""" Cater for all stocks. Each stock is parse one at a time.
"""
self.com_data_allstock_df = pandas.DataFrame()
for stock in self.stock_list:
print 'Processing stock:', stock
self.set_target_stock_url(stock)
self.get_com_data()
self.downloading_csv()
self.process_dataset()
## process the data, group by each symbol and take the last 3-5 years EPS year on year??
def get_trend_data(self):
""" Use for getting trends data of the dataset.
Separate to two separate type. One is looking at gain in yoy gain, which means the gain of EPS eg is higher this year over the last as
compared to the EPS gain of last year over the previous one.
The other is positive gain which look for gain of company over year.
may have accel growth if starting is negative
"""
grouped_symbol = self.com_data_allstock_df.groupby("SYMBOL")
self.hist_company_data_trends_df = pandas.DataFrame()
for label in ['EPS yoy','Revenue yoy','Net income yoy']:
for n in range(9,5,-1):
if n == 9:
prev_data = grouped_symbol.nth(n)[label]
accel_growth_check = (prev_data == prev_data) #for EPS growht increase every eyar
normal_growth_check = (prev_data >0) #for normal increase
continue
current_data = grouped_symbol.nth(n)[label]
accel_growth_check = accel_growth_check & (current_data <= prev_data)
normal_growth_check = normal_growth_check & (current_data >0)
prev_data = current_data
accel_growth_check = accel_growth_check.to_frame().rename(columns = {label: label + ' 4yr_accel'}).reset_index()
normal_growth_check = normal_growth_check.to_frame().rename(columns = {label: label + ' 4yr_grow'}).reset_index()
both_check_df = pandas.merge(accel_growth_check, normal_growth_check, on = 'SYMBOL' )
if len(self.hist_company_data_trends_df) ==0:
self.hist_company_data_trends_df = both_check_df
else:
self.hist_company_data_trends_df = pandas.merge(self.hist_company_data_trends_df, both_check_df, on = 'SYMBOL' )
def modify_stock_sym_in_df(self):
""" Modify the stock sym in df especially for the Singapore stock where it require .SI to join in some cases.
"""
self.hist_company_data_trends_df['SYMBOL']= self.hist_company_data_trends_df['SYMBOL'].astype(str) +'.SI'
def strip_additional_parm_fr_stocklist(self, stocklist, add_parm = '.SI'):
""" Strip the addtional paramters from the stock list. True in case where the input is XXX.SI and morning star do not required the additioanl SI.
Args:
stocklist (list): list of stock sym.
Kwargs:
add_parm (str): string to omit (.SI)
"""
return [re.search('(.*)%s'%add_parm, n).group(1) for n in stocklist]
if __name__ == '__main__':
choice = 4
if choice ==2:
pp = MS_StatsExtract()
pp.set_stocklist(['BN4','BS6','N4E','U96'])
pp.get_com_data_fr_all_stocks()
pp.get_trend_data()
pp.modify_stock_sym_in_df()
print pp.hist_company_data_trends_df